
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Durable CPVC and FRP Pipes for Superior Resistance and Longevity
Combining Durability and Resistance The Role of CPVC and FRP Pipes
In the modern construction and manufacturing sectors, the demand for materials that guarantee longevity and resistance under various conditions has never been higher. Among the options available, CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) and FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) pipes stand out due to their unique properties that cater to a wide range of applications. This article explores how the combination of CPVC and FRP pipes can deliver both durability and resistance, making them ideal choices for various industrial and commercial applications.
CPVC pipes are known for their excellent resistance to corrosion, making them a preferred choice in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is common. The chlorination process enhances the physical and chemical properties of PVC, enabling CPVC pipes to withstand higher temperatures and pressures. This makes them particularly advantageous in hot water distribution systems, where traditional materials may fail. Moreover, CPVC is inherently lightweight, which facilitates easier installation and reduced transportation costs, thereby enhancing overall project efficiency.
On the other hand, FRP pipes offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, resulting from their composite nature. Composed of a matrix of plastic reinforced with fibers, typically glass or carbon, FRP pipes exhibit immense tensile strength and rigidity, while still being lightweight. This combination is imperative in applications where high stress is a concern, such as in chemical processing plants and offshore oil and gas operations. Additionally, FRP’s resistance to a wide range of chemicals further broadens its applicability, allowing it to be utilized in situations where other materials might degrade.
cpvc and frp pipes combine durability and resistance.
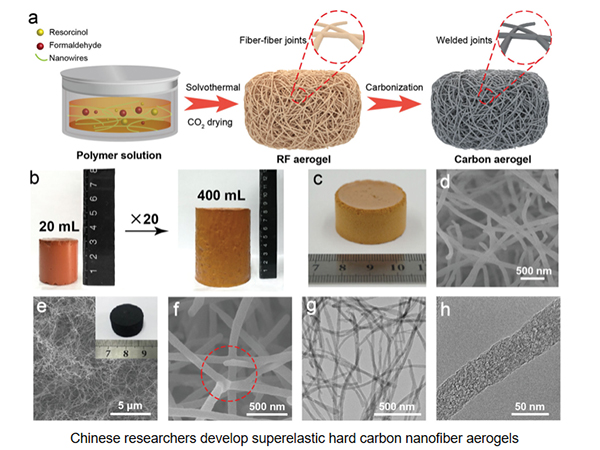
When combined, CPVC and FRP pipes create a synergistic effect that amplifies their individual strengths. The durability of CPVC enhances the already robust nature of FRP, resulting in a pipe system that can endure extreme conditions while minimizing downtime for repairs and replacement. Moreover, the integration of these two materials allows for the creation of hybrid systems that can be tailored to specific requirements, whether it be for chemical resistance, thermal insulation, or structural integrity.
Another important aspect to consider is the environmental impact of using CPVC and FRP pipes. Both materials can contribute to sustainable construction practices. CPVC pipes, for instance, have a lower life cycle impact compared to traditional materials due to their energy-efficient production process. Similarly, FRP’s durability leads to a longer service life, reducing the frequency of replacements and consequently lowering waste production.
In addition to their physical and performance attributes, CPVC and FRP pipes are also cost-effective choices in the long run. While the initial investment may be higher than that for conventional piping materials, the durability, lower maintenance costs, and extended lifespan ultimately result in significant savings. As industries increasingly shift towards more sustainable practices, the economic benefits of maintaining efficient, durable piping systems become paramount.
In conclusion, the combination of CPVC and FRP pipes offers an unrivaled solution for industries seeking durability and resistance in their fluid transport systems. By leveraging the unique properties of both materials, businesses can ensure reliable operations under the most challenging conditions. As the demand for advanced materials continues to grow, CPVC and FRP pipes represent a forward-thinking approach that meets the needs of a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
Latest news
-
Exploring the Benefits of Top Hammer Drifter Rods for Enhanced Drilling PerformanceNewsJun.10,2025
-
High-Precision Fiberglass Winding Machine for GRP/FRP Pipe Production – Reliable & Efficient SolutionsNewsJun.10,2025
-
FRP Pipes & Fittings for Shipbuilding - Corrosion-Resistant & LightweightNewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium FRP Flooring Solutions Durable & Slip-ResistantNewsJun.09,2025
-
Premium Fiberglass Rectangular Tanks Durable & Lightweight SolutionNewsJun.09,2025
-
Tapered Drill String Design Guide Durable Performance & UsesNewsJun.09,2025









