
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
frp panel
Understanding FRP Panels A Comprehensive Overview
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) panels are innovative materials increasingly used in various industries due to their unique properties and advantages. Comprising a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers, these panels offer a perfect blend of strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. This article delves into the composition, benefits, and applications of FRP panels, highlighting why they have become a favored choice in modern construction and manufacturing.
Composition of FRP Panels
FRP panels are constructed from a thermosetting resin, typically polyester or vinyl ester, combined with glass fibers. The fibers are the reinforcing phase, providing the necessary strength and rigidity, while the resin acts as a binder allowing for shape retention and protection from external elements. The manufacturing process usually involves techniques such as hand lay-up, spray-up, or vacuum infusion, which contribute to the overall quality and durability of the final product.
Advantages of FRP Panels
1. Corrosion Resistance One of the most significant advantages of FRP panels is their excellent resistance to corrosion. Unlike traditional materials such as wood or steel, which can deteriorate when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme weather conditions, FRP panels remain intact, making them ideal for use in environments prone to corrosion.
2. Lightweight and Durable Despite their lightweight nature, FRP panels exhibit a high strength-to-weight ratio, meaning they can withstand significant loads without being cumbersome. This characteristic simplifies transportation and installation, reducing overall project costs.
3. Thermal Insulation FRP panels possess excellent thermal insulation properties, helping to maintain stable indoor temperatures and reducing energy costs. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications involving temperature-sensitive products or environments.
4. Aesthetic Flexibility Available in a variety of colors, patterns, and finishes, FRP panels offer considerable design versatility. Manufacturers can fabricate panels that resemble traditional materials, such as wood or stone, allowing architects and designers to achieve desired aesthetics without sacrificing functionality.
5. Low Maintenance Given their resilience and robustness, FRP panels require minimal maintenance. Their surface can be easily cleaned, and they do not need regular treatments or coatings like paint, which can fade or peel over time.
frp panel
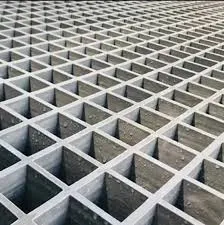
Applications of FRP Panels
FRP panels find utility in numerous sectors, including
- Construction In buildings, FRP panels serve as exterior cladding, interior walls, and roofing materials. Their resistance to moisture and termites makes them suitable for areas prone to damp conditions.
- Transportation In the automotive and aerospace industries, FRP panels are used to manufacture lightweight components that improve fuel efficiency without compromising structural integrity.
- Food Processing The hygiene and easy cleanability of FRP panels make them ideal for food processing facilities. Their non-porous surface prevents bacterial growth, ensuring compliance with health regulations.
- Marine Applications With their exceptional corrosion resistance, FRP panels are widely employed in the marine industry for boat construction and repairs, where exposure to saltwater can significantly damage conventional materials.
- Renewable Energy FRP panels are increasingly being used in the manufacture of wind turbine blades and other renewable energy applications due to their lightweight and durable properties.
Conclusion
In summary, FRP panels represent a significant advancement in material technology, offering a combination of strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors that traditional materials often lack. Their versatility ensures they can cater to various needs across multiple industries, making them an indispensable asset in modern manufacturing and construction. As technology advances, the applications and benefits of FRP panels are likely to expand further, solidifying their role in sustainable and efficient building practices.









