
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Feb . 17, 2025 17:04
Back to list
grp car body
GRP, standing for Glass Reinforced Plastic, has become a significant material in the manufacturing of car bodies. Known for its robustness and versatility, GRP is becoming a go-to choice for automotive designers and manufacturers aiming to balance weight, strength, and cost-effectiveness. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the applications, advantages, and future of GRP car bodies, ensuring readers develop a full understanding of its burgeoning prominence in modern automotive engineering.
From a sustainability perspective, GRP contributes to eco-friendly automotive manufacturing. The lightweight characteristic of GRP leads to improved fuel efficiency, thereby reducing the carbon footprint of vehicles. Additionally, the recycling potential of GRP materials is being actively explored, with significant strides made in creating a closed-loop lifecycle. As environmental concerns become increasingly central to consumer and regulatory pressures, GRP presents a forward-thinking solution that aligns with global sustainability goals. In terms of authoritative development in the GRP niche, continuous research and technological advancements are paving the way for its expanded use. Collaborative efforts among automotive engineers, material scientists, and manufacturing experts are driving innovations that enhance GRP’s performance properties. These partnerships are also addressing challenges such as scalability and cost-effectiveness, positioning GRP as a competitive alternative to traditional automotive body materials. Trustworthiness is further bolstered by rigorous testing and certification processes that GRP materials undergo before they can be approved for automotive use. Standards and regulations set by automotive governing bodies ensure that GRP products meet stringent safety and quality requirements. This compliance with industry regulations serves as a testament to GRP’s reliability and builds confidence among manufacturers and consumers alike. While the journey of GRP car bodies is still evolving, the trajectory indicates a bright future. With advancements in production techniques and the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and sustainable vehicles, GRP stands to gain a prominent foothold in the automotive industry. It represents a convergence of technological innovation and material science, yielding a product that addresses modern automotive challenges while paving the way for future solutions. In conclusion, GRP car bodies epitomize the intersection of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in automotive manufacturing. Their increasing adoption by world-class manufacturers stands as a testament to their unmatched advantages. As more research and development unfold, GRP’s role in shaping the future of vehicles promises to be both significant and enduring. For industry stakeholders, keeping abreast of these developments is crucial, ensuring they remain competitive and responsive to emerging trends and consumer demands.
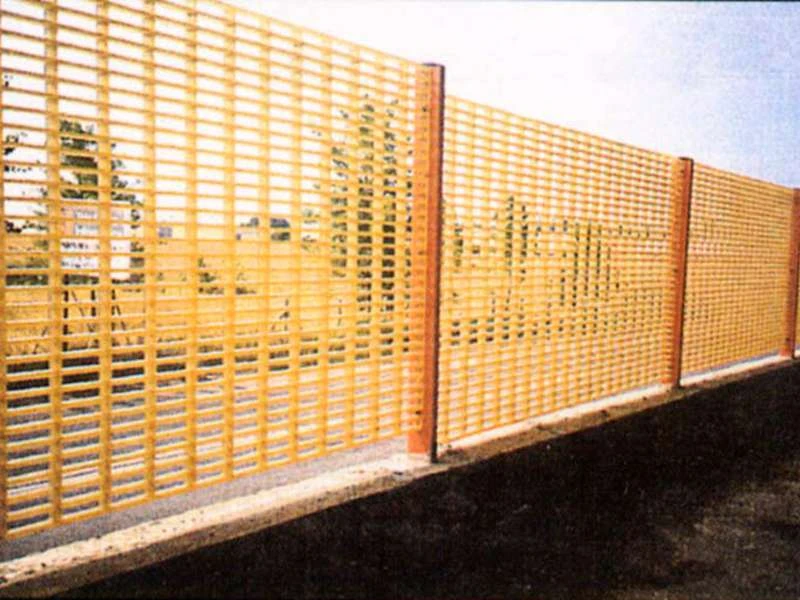

From a sustainability perspective, GRP contributes to eco-friendly automotive manufacturing. The lightweight characteristic of GRP leads to improved fuel efficiency, thereby reducing the carbon footprint of vehicles. Additionally, the recycling potential of GRP materials is being actively explored, with significant strides made in creating a closed-loop lifecycle. As environmental concerns become increasingly central to consumer and regulatory pressures, GRP presents a forward-thinking solution that aligns with global sustainability goals. In terms of authoritative development in the GRP niche, continuous research and technological advancements are paving the way for its expanded use. Collaborative efforts among automotive engineers, material scientists, and manufacturing experts are driving innovations that enhance GRP’s performance properties. These partnerships are also addressing challenges such as scalability and cost-effectiveness, positioning GRP as a competitive alternative to traditional automotive body materials. Trustworthiness is further bolstered by rigorous testing and certification processes that GRP materials undergo before they can be approved for automotive use. Standards and regulations set by automotive governing bodies ensure that GRP products meet stringent safety and quality requirements. This compliance with industry regulations serves as a testament to GRP’s reliability and builds confidence among manufacturers and consumers alike. While the journey of GRP car bodies is still evolving, the trajectory indicates a bright future. With advancements in production techniques and the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and sustainable vehicles, GRP stands to gain a prominent foothold in the automotive industry. It represents a convergence of technological innovation and material science, yielding a product that addresses modern automotive challenges while paving the way for future solutions. In conclusion, GRP car bodies epitomize the intersection of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in automotive manufacturing. Their increasing adoption by world-class manufacturers stands as a testament to their unmatched advantages. As more research and development unfold, GRP’s role in shaping the future of vehicles promises to be both significant and enduring. For industry stakeholders, keeping abreast of these developments is crucial, ensuring they remain competitive and responsive to emerging trends and consumer demands.
Related Products









