
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Feb . 16, 2025 06:33
Back to list
molded fiberglass grating
Molded fiberglass grating has become a cornerstone in modern industrial design, offering a unique blend of durability, versatility, and resilience. Understanding the extensive applications and benefits of molded fiberglass grating is crucial for industries looking to optimize long-term performance and safety.
In terms of industry application, molded fiberglass grating is versatile. In the construction industry, it serves as a reliable component for roof walkways and scaffolding. In the transportation sector, it’s used in rail platforms and airport maintenance areas. In addition, in the food and beverage industry, it provides a hygienic, durable surface that withstands high-pressure cleaning and harsh chemical sanitization. Despite its lightweight and easy-to-install nature, molded fiberglass grating does not compromise on strength. It offers a load-bearing capacity that rivals traditional materials, making it suitable for applications that involve substantial weight loads, such as heavy machinery platforms or storage areas in warehouses. Environmental impact is another arena where molded fiberglass grating excels. Unlike materials prone to rust and breakdown, leading to frequent replacements and increased waste, fiberglass has a long lifecycle. This durability minimizes the frequency of replacement, thus reducing landfill contributions and resource consumption. Additionally, fiberglass grating can be made with resins that are non-toxic and environmentally friendly, bolstering its appeal in eco-conscious projects. From a cost perspective, while the initial investment for molded fiberglass grating may be higher than traditional materials, its long-term savings, due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs, make it an economically sound choice. Companies looking to invest in sustainable, cost-effective infrastructure will find molded fiberglass grating a wise long-term investment. Equipped with these benefits, choosing molded fiberglass grating for industrial applications becomes an exercise in foresight and efficiency. Businesses across sectors are discovering the transformative impact of this versatile material. As industries continue to prioritize safety, durability, and sustainability, the demand for molded fiberglass grating is expected to rise, reaffirming its position as a vital component in industrial design and engineering.

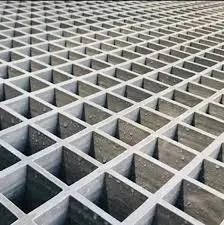
In terms of industry application, molded fiberglass grating is versatile. In the construction industry, it serves as a reliable component for roof walkways and scaffolding. In the transportation sector, it’s used in rail platforms and airport maintenance areas. In addition, in the food and beverage industry, it provides a hygienic, durable surface that withstands high-pressure cleaning and harsh chemical sanitization. Despite its lightweight and easy-to-install nature, molded fiberglass grating does not compromise on strength. It offers a load-bearing capacity that rivals traditional materials, making it suitable for applications that involve substantial weight loads, such as heavy machinery platforms or storage areas in warehouses. Environmental impact is another arena where molded fiberglass grating excels. Unlike materials prone to rust and breakdown, leading to frequent replacements and increased waste, fiberglass has a long lifecycle. This durability minimizes the frequency of replacement, thus reducing landfill contributions and resource consumption. Additionally, fiberglass grating can be made with resins that are non-toxic and environmentally friendly, bolstering its appeal in eco-conscious projects. From a cost perspective, while the initial investment for molded fiberglass grating may be higher than traditional materials, its long-term savings, due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs, make it an economically sound choice. Companies looking to invest in sustainable, cost-effective infrastructure will find molded fiberglass grating a wise long-term investment. Equipped with these benefits, choosing molded fiberglass grating for industrial applications becomes an exercise in foresight and efficiency. Businesses across sectors are discovering the transformative impact of this versatile material. As industries continue to prioritize safety, durability, and sustainability, the demand for molded fiberglass grating is expected to rise, reaffirming its position as a vital component in industrial design and engineering.
Related Products









